Florida International University, Miami, FL, USA
PARKING: The 3D-PEIM Symposium is paying for the parking if your vehicle is registered at this link before arrival. Click here for more information.

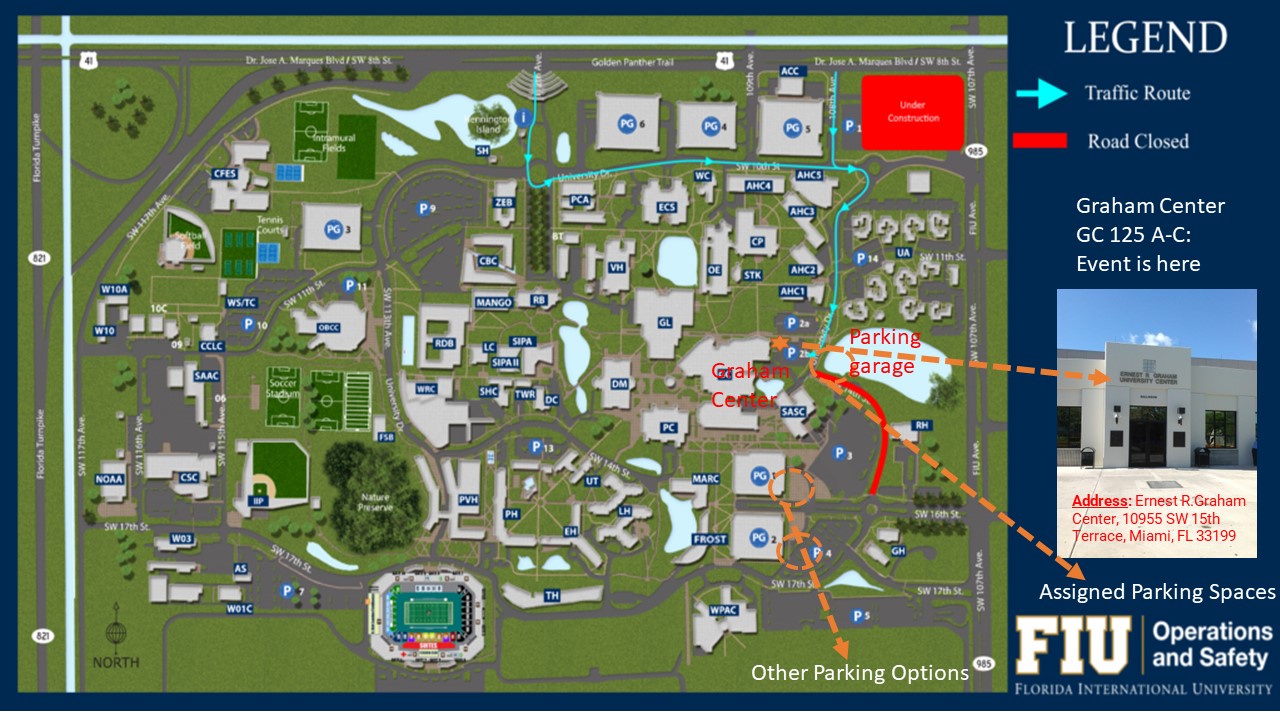
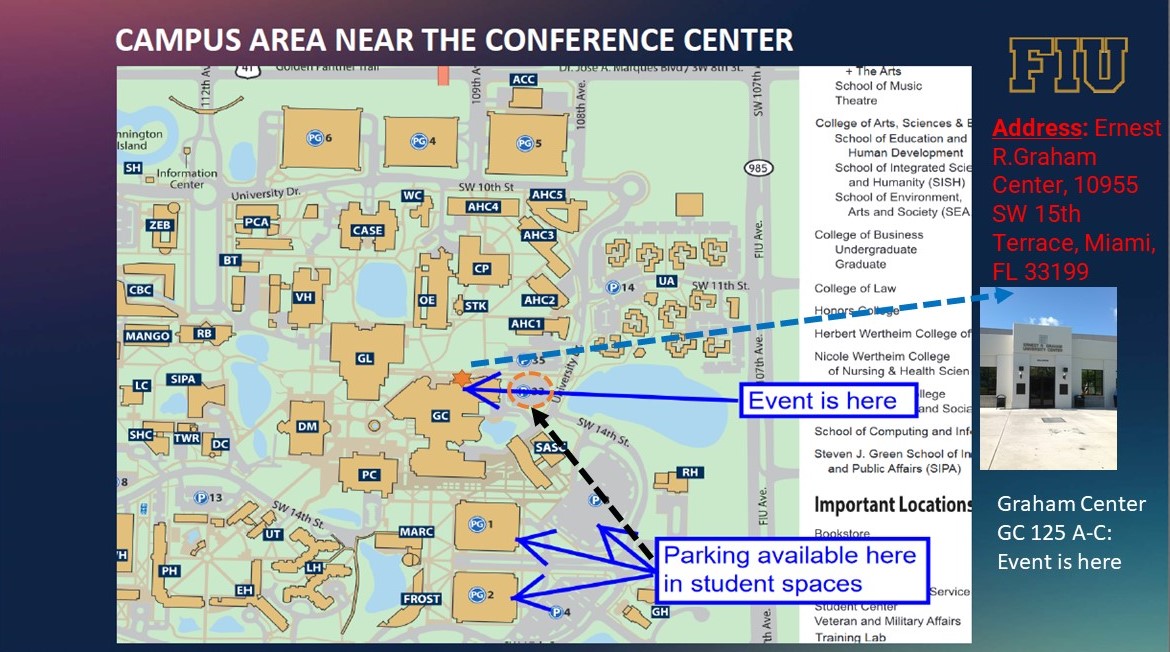
Address: Ernest R.Graham Center, 10955 SW 15th Terrace, Miami, FL 33199
When coming to the Graham Center by Taxi or Uber/Lift give them the address above then enter the building through the ballroom entrance on the map.
Ballroom entrance is adjacent (to the East) to North Entrance; If you enter from the South entrance, you need to work to the North exit, exit the building, walk to the right (East) and enter through the Ballroom Entrance.

Florida International University is a vibrant, student-centered public research university, ideally located in Miami, committed to learning, research, entrepreneurship, innovation, and creativity so that our graduates are prepared to succeed in a global market. FIU’s Modesto Maidique Campus (MMC) is readily accessible from Miami and Fort Lauderdale international airports. Miami International Airport (MIA) is approximately 11 miles from MMC. Fort Lauderdale-Hollywood International Airport (FLL) is approximately 37 miles from MMC.
The FIU College of Engineering and Computing offers a complete range of fully accredited engineering bachelor’s, master’s, and doctoral degree programs in biomedical, civil and environmental, electrical and computer, mechanical and materials engineering; construction management; and computing and information sciences. FIU’s College of Engineering and Computing is home to nearly 8,000 engineering and computing students, including nearly 1,100 graduate students. In AY2021, the college graduated nearly 2,000 engineers and computer scientists. The college was ranked No. 1 in the U.S. in awarding bachelor’s degrees to Hispanic students and No. 11 in awarding bachelor’s degrees to African Americans by the American Society for Engineering Association (ASEE) in 2021. With an annual budget of $60M, the university hosts 50+ centers, institutes, and labs that include: Advanced Packaging for power modules and integration, Advanced Materials Engineering Research Institute, Energy Systems Research Laboratory, Energy, Power & Sustainability Laboratory, and several others.
The university is the home for leading faculty experts in the area of power electronics. Selected topics in this area are described below:
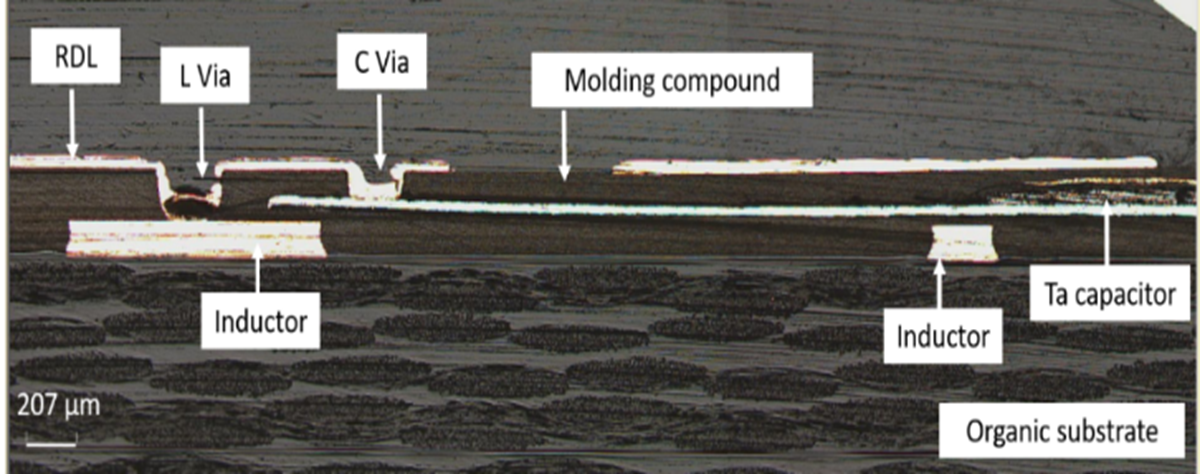
The Electronic and Bioelectronic Packaging lab at FIU drives several key innovations in next-generation manufacturing technologies for computing, power, RF, and biomedical market segments. Key examples include embedded power passive components, with multiple technologies at the translational stage through industry partnerships. Leading-edge magnetic components and the highest power densities with on-chip and embedded capacitors are demonstrated. The lab is also the first to demonstrate fan-out flex embedding, multiferroic wireless power components in thin fan-out packages, and embedded wireless sensors with such packages.
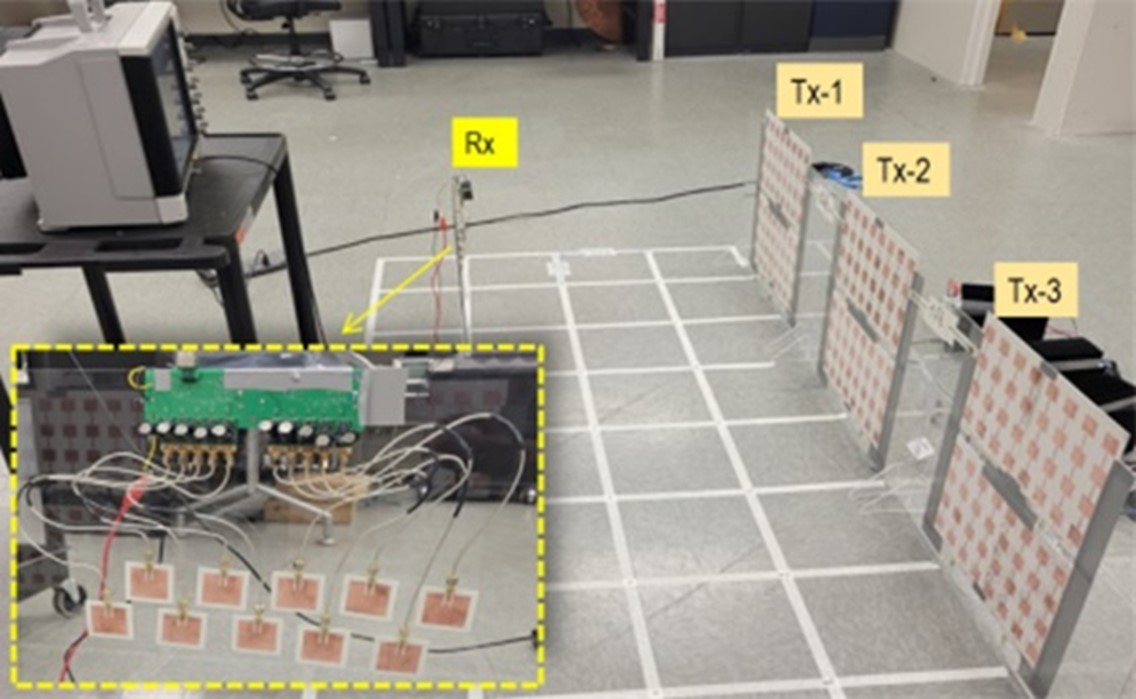
FIU excels in Wireless Power Transfer technologies to seamlessly charge mobile devices while the user is mobile using the Ad-hoc mesh networking method. This disruptive technology holds the unique advantage of providing recharging of moving targets similar to the cellular concept used in WiLAN, as opposed to prior wireless charging attempts, which only allow hotspot-based charging. Specifically, the RFCOM team has demonstrated the charging of a popular smartphone using the proposed system in the radiating near field zone of the transmitter antennas, while the user is free to move in the space on the meshed network.
The Advanced Materials Engineering Research Institute is the home for developing future technologies by combining open-access, and state-of-the-art fabrication, analytical and packaging tools with innovative research ideas. AMERI is an enabler of research and technology development in the field of sensors, bio-electronics, batteries, solar cells, electronic packaging, corrosion, coatings and composites, aerospace materials, biomaterials, and ceramics.
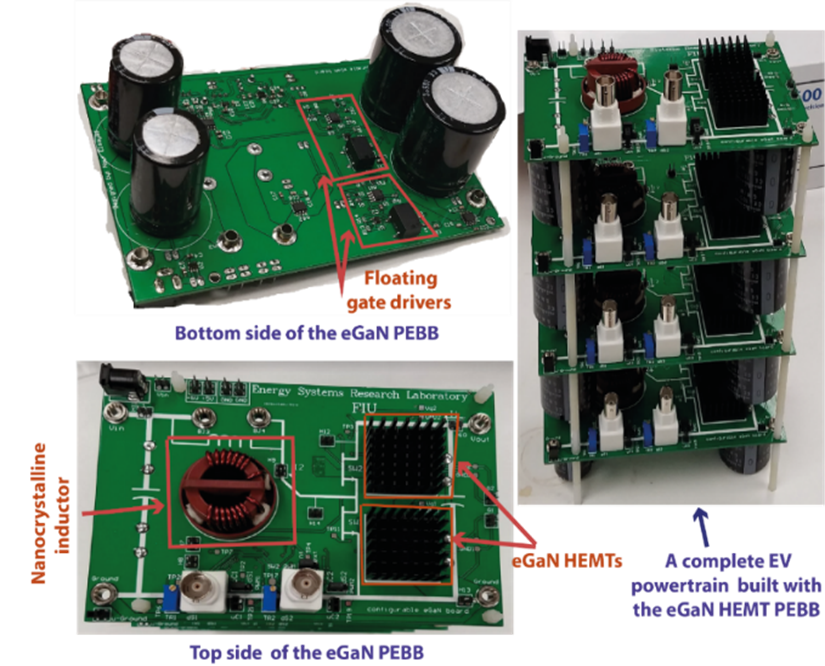
The Energy System Research Laboratory (ESRL) at FIU has been creating major innovations in new dc-dc converter topologies. The converters have reduced voltage stresses on the switches. Three of them are unidirectional step-up converters with universal input voltage, making them excellent candidates for photovoltaic and fuel cell applications. The other three converters are bidirectional dc-dc converters with wide voltage conversion ratios. These converters are excellent candidates for applications that require bidirectional power flow capability. In addition, the wide voltage conversion ratios of these converters can be utilized for applications such as energy storage systems with wide voltage swings.
The FIU Smart Grid Testbed is located at Energy Systems Research Laboratory facility in the Department of Electrical Engineering, College of Engineering and Computing at Florida International University in Miami, Florida. It is a state-of-the-art hardware-software platform for research and development, component evaluation, as well as educational activities.
- This reduced-scale power system was created and built to implement new technologies and products required for Smart Grid development.
- Technologies related to increased electric vehicle penetration, microgrid implementations, advanced metering, communication and security, and cyber-physical systems are featured on this testbed.
- This Smart Grid testbed has the capabilities to emulate bulk generation, distributed generation, energy storage of different types, and study their utilization.
- The Smart Grid Testbed has several physical, data, network communication, and security layers.
- One of the main focuses in building this testbed is on the communication and distributed real-time control issues.
- The communication infrastructure allows the connection of all components to control points.
ESRL at FIU also employs several microgrids to incorporate the integration of wind, solar, and energy storage systems. Renewable energy is a complementary source that is implemented on the testbed in the form of 3 .C.D.C. microgrids. This testbed includes the latest technologies for energy storage systems, mainly batteries, supercapacitors/ ultracapacitors, and flywheels.
Hybrid AC-DC Plug-in Electric Vehicle Car Park Emulator
- On the Smart Grid testbed, operation, implementation, control, and energy management case studies can be conducted on plug-in electric vehicles (PEV) using the smart charging station emulator.
- Smart energy management algorithms are implemented considering commercially sustainable energy resources.
- A combination of energy storage, power electronics, and a power system emulator allows for designing and implementing highly-efficient components for future PEV car parks.
- This enables the study of the utility grid reaction in terms of voltage, loss, and loading issues.
- Vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V) and vehicle-to-grid (V2G) services provide voltage assessments, frequency regulations, and economics for future parking garages.